What is an-entity & it's type in DBMS? explain with proper Diagram - Computer science fundamentals tutorial
Entity set & it's types
PDF version of this post also available. to download the click the link is given at the end of this post.
1.What is entity?
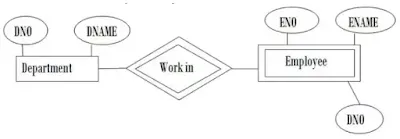
Ans/- An entity can be a real word object either animated or inanimate that can be easily identifiable. An entity in a database is represented as a set of attributes. Each entity has a different sets of values for some set of attributes and this is how entity seems to be distinct from other entities. In relational model, an entity is represented as a row, tuple or a record.
Ans/- An entity can be a real word object either animated or inanimate that can be easily identifiable. An entity in a database is represented as a set of attributes. Each entity has a different sets of values for some set of attributes and this is how entity seems to be distinct from other entities. In relational model, an entity is represented as a row, tuple or a record.
2.What is Entity set?
Ans/- An entity set is a group of similar kind of entities. It may contain entities with attributes sharing similar values. Entities are represents by their properties which also called attributes.
Ans/- An entity set is a group of similar kind of entities. It may contain entities with attributes sharing similar values. Entities are represents by their properties which also called attributes.
Type of entity: -Entities are two types. there are a) weak entity b) strong entity. now we explain these entities with example and also their difference between them.
Weak entity: - A weak entity is a type of entity which doesn’t have its key attribute. It can be identified uniquely by considering by consisting primary key of another entity. It represented by double rectangular box. Weak relation represent by double diamond box.
Difference between strong and weak entity: -
click here for PDF version of this post
PDF of What is an entity & its type in DBMS
To know about Cardinality & its type in details visit my blog site given below
https://programminglanguagepoint.blogspot.com/2020/06/what-is-cardinality-or-binary.html
PDF of What is an entity & its type in DBMS
To know about Cardinality & its type in details visit my blog site given below
https://programminglanguagepoint.blogspot.com/2020/06/what-is-cardinality-or-binary.html



Comments
Post a Comment
please subscribe my blog and let me suggest how I improve this site