Loop
control structure
**note**
PDF version of this post also available. To get the PDF click the link given at the end of this post.
There are three types of loop control statement-
1. For loop.
2. While loop.
3. Do - while loop.
1. for loop: - The For loop
provides a mechanism to repeat a task until a particular condition is true. For
loop is usually known as determinate or definite loop because the
programmer knows exactly how many times the loop will repeat. The number of
times the loop has to be executed can be determined mathematically by checking
the logic of the loop.
Syntax of for loop :
-
For(initialcondition;<endcondition>;increment/decrement)
{
Statement
block;
}
}
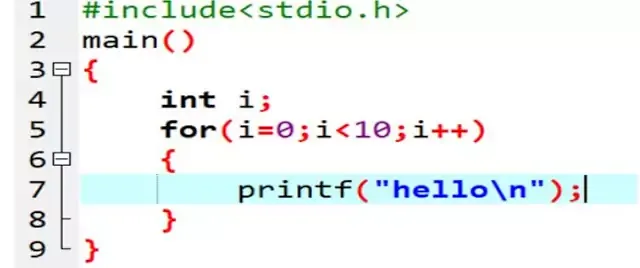
Explanation of this program:
-
Here we can see in For loop, loop started from i=0.
Its end condition is i<10.
In this loop it started execute from i=0. After first
iteration it incremented to one and repeat same task and print ‘hello’ second
time. It continue to execute until initial condition greater than 10.when it
greater than 10 loop stop execute
Output: -
While loop: - The while loop provides a mechanism to repeat one or more statements while a particular condition is true.
While loop: - The while loop provides a mechanism to repeat one or more statements while a particular condition is true.
Syntax of while loop:
-
Statement x;
While(condition)
{
Statement
block;
}
Statement y;
Explanation of this program:-
At first initialize i=1.
Then started while loop with ’i<=10’ condition.
Initially i=1 and is less than 10,i.e. condition is
true,so in the loop the value i is printed and condition is update so that with
every execution of the loop. The loop execute until value of i greater than equal to 10.
Do-while loop:-
The do – while loop is similar to the while loop. The
only difference is that in a do-while loop, the test condition evaluated at the
end of the loop. Now that the test condition is evaluated at the end which
means that the body of the loop gets executed at least one time even condition
is false.
Syntax of the Do-while loop:
-
statement x;
do
{
statement block;
}while(condition);
statement y;
Output: -
The major disadvantage of Do-while loop is that always execute at least once, even if the user enters some invalid data, the loop will execute.
The major disadvantage of Do-while loop is that always execute at least once, even if the user enters some invalid data, the loop will execute.
Comparison
of loop structure statements: -






Thats really great blog , thanks for sharing to us.
ReplyDeleteGet all type digital machine like as AM.CO.ZA V-Series™ High-Pressure High-Speed USB Vinyl Cutters Vinyl Cutter