Decision Control Statement
**NOTE**
PDF version of this post also available. to get the PDF of Decision Control Statements in C click the link given at end of this post.
PDF version of this post also available. to get the PDF of Decision Control Statements in C click the link given at end of this post.
All statements written in a program are executed from top to bottom one by one. Control statements are used to execute/transfer the control from one part of the program to the another depending on condition. These statements are also called conditional statement. There are two types of decision control statements-
1) If-else statement.
2)Switch statement.
If-else statements has three types. They are
i) normal if-else statement.
ii)else-if statement.
iii) nested if-else statement.
If-else statement
The if statement plays a vital role in conditional branching. Its usage is very simple, the test expression is evaluated, if the result is true, the statement(s) followed by the expression is executed else if the expression is false, the statement is skipped by the compiler.
Syntax of if-else statement
If(condition)
{
true block
}
else
{
false block
}
Example: -
Write a c program to find out biggest of two numbers.
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
int x,y,big;
printf("enter the value for x = ");
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("enter the value for y = ");
scanf("%d", &y);
if(x>y)
{
big=x;
printf("biggest of given two number is %d",big);
}
else
{
big=y;
printf("biggest of given two number is %d",big);
}
}
Explanation of this example
1. take two number as input.
2. after taking input it started the if block. In If block it checks x with y. if isn't bigger than x then the value of x assign into big & print this as output.
3. otherwise in else block the value of y assign into big & print this as output.
Output
Example of else-if
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
int num1,num2,num3,big;
printf("enter the value for num1:");
scanf("%d",&num1);
printf("enter the value for num2:");
scanf("%d",&num2);
printf("enter the value for num3:");
scanf("%d",&num3);
if(num1>num3)
{
if(num1>num3)
big=num1;
else
big=num3;
}
else
{
if(num2>num3)
big=num2;
else
big=num3;
}
printf("biggest no=%d",big);
}
Program explanation:-
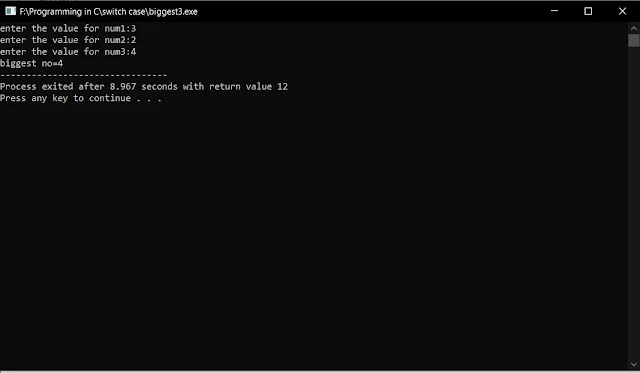
1. Take the three numbers and store it in the variables a,b,c respectively.for example we take num1=3,num2=2, num3= 4
2. Firstly check if the num1 is greater than num2.
3. If it is, then check if it is greater than num3.
4. If it is, then print the output as “num1 is the greatest among three”.
5. Otherwise print the ouput as “num3 is the greatest among three”.
6. If the num1 is not greater than num2, then check if num2 is greater than num3.
7. If it is, then print the output as “num2 is the greatest among three”.
8. Otherwise print the output as “num3 is the greatest among three”.
Output of this program
main()
{
int num1,num2,num3,big;
printf("enter the value for num1:");
scanf("%d",&num1);
printf("enter the value for num2:");
scanf("%d",&num2);
printf("enter the value for num3:");
scanf("%d",&num3);
if(num1>num3)
{
if(num1>num3)
big=num1;
else
big=num3;
}
else
{
if(num2>num3)
big=num2;
else
big=num3;
}
printf("biggest no=%d",big);
}
Program explanation:-
1. Take the three numbers and store it in the variables a,b,c respectively.for example we take num1=3,num2=2, num3= 4
2. Firstly check if the num1 is greater than num2.
3. If it is, then check if it is greater than num3.
4. If it is, then print the output as “num1 is the greatest among three”.
5. Otherwise print the ouput as “num3 is the greatest among three”.
6. If the num1 is not greater than num2, then check if num2 is greater than num3.
7. If it is, then print the output as “num2 is the greatest among three”.
Output of this program

If-else-if /nested if-else statement
The if-else-if construct works in the same way as a normal if statement If-else-if construct is also known as nested if-else construct.
Syntax of nested if-else statement
if(condition)
{
if(condition)
{
statement block
}
else
{
statement block
}
}
else
{
if(condition)
{
statement block
}
else
{
statement block
}
}
Example of this statement
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
int a,b,c,big;
printf("enter any three no");
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
if(a>b)
{
if(a>c)
big=a;
else
big=c;
}
else
{
if(b>c)
big=b;
else
big=c;
}
printf("biggest no=%d",big);
}
Output of this program
Switch case statement
A switch case statement is a multi way decision statement that is a simplified version of an if -else block that evaluate only one variable.
Syntax of Switch case statement
switch(expression)
{
case(label name):
..........
break;
case(label name):
.........
break;
default:
break;
}
example of switch case
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
int m, i;
printf("\n Enter any number: ");
scanf("%d", &m);
i = m%10;
switch(i)
{
case 10:
case 9:
printf("O");
break;
case 8:
printf("E");
break;
case 7:
printf("A");
break;
case 6:
printf("B");
break;
case 5:
printf("C");
break;
case 4:
printf("D");
break;
default:
printf("F");
}
}
main()
{
int m, i;
printf("\n Enter any number: ");
scanf("%d", &m);
i = m%10;
switch(i)
{
case 10:
case 9:
printf("O");
break;
case 8:
printf("E");
break;
case 7:
printf("A");
break;
case 6:
printf("B");
break;
case 5:
printf("C");
break;
case 4:
printf("D");
break;
default:
printf("F");
}
}
Explanation of this program
Case 1:- If the user is Over smart then there is a condition that if the mark given by the user is greater than 100 then our program display the Message "Don't Be Smart Enter your Marks Between Limit" or else perform the Else part.
Enter the Mark:- 1000
Output:- Don't Be Smart Enter your Marks Between Limit.
Case 2:- If the user is entering the marks between the 0 to 100 and then particular grade portion will be executed and display the output in Console screen.
Enter the Mark:- 95
Output:-Your Grade Is: A or Excellent
This operation performs same for Grade B, C, D.
Case 3:- If Enter marks are not fulfilled the cases requirement than the program will perform the default case.
Enter the Mark:-25
Output:-You Grade Is: F or Fail
Enter the Mark:- 1000
Output:- Don't Be Smart Enter your Marks Between Limit.
Case 2:- If the user is entering the marks between the 0 to 100 and then particular grade portion will be executed and display the output in Console screen.
Enter the Mark:- 95
Output:-Your Grade Is: A or Excellent
This operation performs same for Grade B, C, D.
Case 3:- If Enter marks are not fulfilled the cases requirement than the program will perform the default case.
Enter the Mark:-25
Output:-You Grade Is: F or Fail



Comments
Post a Comment
please subscribe my blog and let me suggest how I improve this site